SEO Question: Many people say write naturally for SEO, but what does that mean?
SEO Answer: About a month and a half ago the New York Times published an article by Steve Lohr titled This Boring Headline Is Written for Google. The article flits with the idea of writing newspaper articles with Google in mind. That story got a decent amount of buzz because newspapers usually do not put much consideration into search engine marketing.
Old School Search Engine Optimization:
A few years ago you could do SEO like this:
- start your page title with your keyword or keyword phrase
- include that keyword phrase on most every heading or subheading on that page
- link to the page sitewide with that same keyword in the anchor text
- build a ton of links from external locations, with most (or all) of them containing that keyword phrase
Does Old School Still Work?
For MSN (and, to some extent, Yahoo!) you could still use a somewhat similar keyword stuffing philosophy and see outstanding results, but the problem with the stick my core phrase everywhere SEO method! is that Google does not want to show the most optimized content. They want to show the most relevant content.
As noted above in the New York Times article, most news articles (and likely most quality web documents) are not heavily focused on concentrating on optimizing for a keyword. Instead they use the natural language associated with that topic.
If too many of your signals are focused on just one word or phrase and you lack the supporting vocabulary in your document you may get filtered out of the search results for your primary keyword targets. It has happened to me several times, and it is a pretty common occurrence, especially for websites that have few authoritative trustworthy votes and try to make up for it by aggressive use of a phrase in the page content.
Here is an example of a snapshot of a spam page I saw ranking for a long tail keyword

The problem is, that page was ranking for Michigan Smoker's Life Insurance when it targeted a way different phrase. The page will never rank for the main phrase it was targeting, so unless they redirect searchers to a more relevant page it is going to be hard for them to convert any visitors that land on a page like that.
Read a bunch of SEO forums and you eventually come across threads with titles like Non optimized pages higher in SERPS than optimized ones???
How to Optimize for Google:
So if old hat optimization is considered overoptimization and/or is potentially detrimental to your rankings what do you do?
You could
- say screw Google they will eventually rank me if I get this keyword on the page 1 more time ;)
- say screw Google I am pulling in plenty of money from Yahoo! and MSN
- not worry about SEO at all
- evolve SEO to a more productive state
Onward and upward I say. How to mix it up to become Google friendly:
- Start the page title with a modifier or couple non keywords instead of placing your primary keyword phrase as the first word of the page title. Example... instead of search engine marketing company start your title with professional search engine marketing...
- Stemming is your friend. Use plural, singular, and ing versions of your keywords. I have seen pages that used a bunch of the plural version filtered out of Google for the plural version but still ranking for the singular version. If you mix it up you can catch both.
- Mix up the anchor text, subheaders and page content. Use semantically related phrases, and, in some cases, write subheaders that are useful for humans even if some of them do not have any keyword phrases in them.
- Make sure each page is somewhat unique and focused in nature.
Semantically related phrases:
If you think of words as having relationships to one another and you visualize optimizing for a keyword as optimizing for a basket of relevant related keywords it will help you draw in relevant related search traffic while also making your page more relevant for its core keywords.
For example, the acronym SEO would have the following as some semantically related phrases
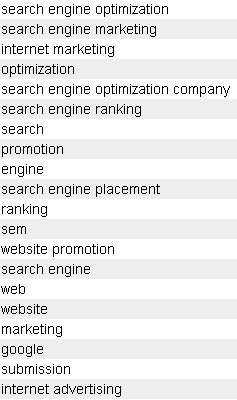
Now you wouldn't necessarily need to get all of those in your page copy, but if a person was writing naturally about the topic of SEO it would be common for many of those kinds of words to appear on the page.
Where do I Find Semantically Related Phrases?
GoRank offers a free semantic research tool. You can also find semantically related phrases by using a Google ~ search, the Google Keyword Tool, clustering engines, or concept pairing tools like Google Sets.
I link to all those tools on my keyword suggestion tool, and here is a background post on latent semantic indexing.
An Over Abundance of Modifiers:
In addition to using words that are semantically related it makes sense to use words that are common modifiers. For example common buying / shopping searches might include words like
- Free shipping
- Coupons
- Coupon
- Deals
- Deal
- Cheap
- Expensive
- Budget
- Bargain
- Bargains
- Affordable
- Low Cost
- Free
- Find
- Get
- Buy
- Purchase
- Locate
- Compare
- Shop
- Shopping
- Search
I created a keyword modifiers spreadsheet with free keyword modifier ideas for a few different search, transaction, and classification types. I might try to expand it a bit if people find it useful.
If it All Sounds Like a Bit Much...
If it seems complex or complicated then don't focus too heavily on the modifiers or semantic related phrases or even your core keyword that much.
First write your article about your topic without even thinking about the search engines. Then go back and tweak it to include relevant modifiers and semantically related phrases. Make sure that you use multiple versions of your primary keyword phrase if it has multiple versions.
To make the page easy to read and to make it easy to add related phrases and alternate versions of your keywords break up the page using many subheaders. Also add leading questions that lead people from one section to the next. For example, I could say did you find this search engine marketing article helpful in your website promotion quest? Do you think it will help you do a become a better search engine optimizer and more holistic internet marketer?
I am a bit tired and I think this was a bit verbose, but hopefully it helps somebody. If not, arggggg... hehehe.


