
There are so many competitive research tools on the market. We reviewed some of the larger ones here but there are quite a few more on the market today.
The truth is that you can really get a lot of good, usable data to give you an idea of what the competition is likely to be by using free tools or the free version of paid tools.
Some of the competitive research tools out there (the paid ones) really are useful if you are going to scale way up with some of your SEO or PPC plans but many of the paid versions are overkill for a lot of webmasters.
Choosing Your Tools
Most tools come with the promises of “UNCOVERING YOUR COMPETITORS BEST _____".
That blank can be links, keywords, traffic sources, and so on. As we know, most competitive research tools are rough estimates at best and almost useless estimates at worst. Unless you get your hands on your competition’s analytics reports, you are still kind of best-guessing. In this example we are looking for the competitiveness of a core keyword.
Best-guessing really isn’t a bad thing so long as you realize that what you are doing is really triangulating data points and looking for patterns across different tools. Keep in mind many tools use Google’s data so you’ll want to try to reach beyond Google’s data points a bit and hit up places like:
The lure of competitive research is to get it done quickly and accurately. However, gauging the competition of a keyword or market can’t really be done with a push of the button as there are factors that come into play which a push-button tool cannot account for, such as:
- how hard is the market to link build for?
- is the vertical dominated by brands and thick EMD’s?
- what is your available capital?
- are the ranking sites knowledgeable about SEO or are they mostly ranking on brand authority/domain authority? (how tight is their site structure, how targeted is their content, etc)
- is Google giving the competing sites a brand boost?
- is Google integrating products, images, videos, local results, etc?
Other questions might be stuff like "how is Google Instant skewing this keyword marketplace" or "is Google firing a vertical search engine for these results (like local" or "is Google placing 3 AdWords ads at the top of the search results" or "is Google making inroads into the market" like they are with mortgage rates.
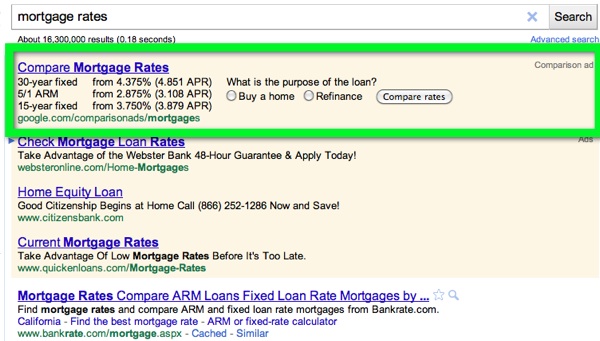
People don't search in an abstract mathematical world, but by using their fingers and eyes. Looking at the search results matters. Quite a bit of variables come into play which require some human intuition and common sense. A research tool is only as good as the person using it, you have to know what you are looking at & what to be aware of.
Getting the Job Done
In this example I decided to use the following tools:
Yep, just 2 free tools.... :)
So we are stipulating that you’ve already selected a keyword. In this case I picked a generic keyword for the purposes of going through how to use the tools. Plug your keyword into Google, flip on SEO for Firefox and off you go!
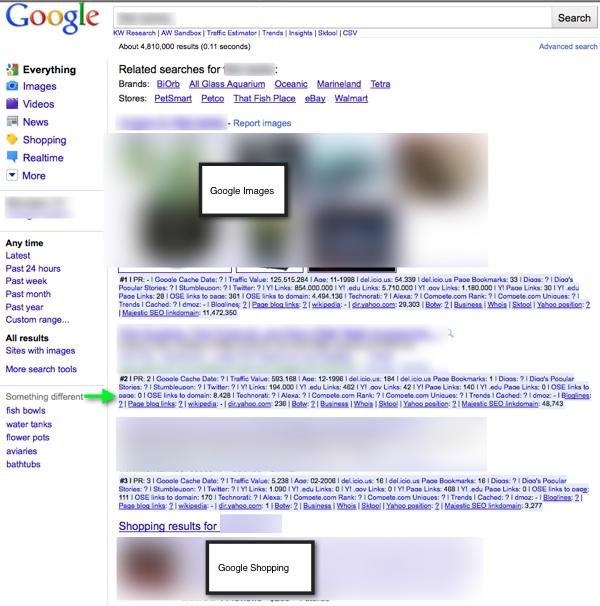
This is actually a good example of where a push button tool might bite the dust. You’ve got Related Search breadcrumbs at the top, Images in the #1 spot, Shopping in the #3 spot, and News (not pictured) in the #5 spot.
So wherever you thought you might rank, just move yourself down a 1-3 spots depending on where you would be in the SERPS. This can have a large effect on potential traffic and revenue so you’ll want to evaluate the SERP prior to jumping in.
You might decide that you need to shoot for 1 or 2 rather than top 3 or top 5 given all the other stuff Google is integrating into this results page. Or you might decide that the top spot is locked up and the #2 position is your only opportunity, making the risk to reward ratio much less appealing.
With SEO for Firefox you can quickly see important metrics like:
- Yahoo! links to domain/page
- domain age
- Open Site Explorer and Majestic SEO link data
- presence in strong directories
- potential, estimated traffic value from SEM Rush
Close up of SEO for Firefox data:

Basically by looking at the results page you can see what other pieces of universal search you’ll be competing with, whether the home page or a sub-page is ranking, and whether you are competing with brands and/or strong EMD’s.
With SEO for Firefox you’ll see all of the above plus the domain age, domain links, page links, listings in major directories, position in other search engines, and so on. This will give you a good idea of potential competitiveness of this keyword for free and in about 5 seconds.
It is typically better & easier to measure the few smaller sites that managed to rank rather than measuring the larger authoritative domains. Why? Well...
Checking Links
So now that you know how many links are pointing to that domain/page you’ll want to check how many unique domains are pointing in and what the anchor text looks like, in addition to what the quality of those links might be.
Due to its ease of use (in addition to the data being good) I like to use Open Site Explorer from SeoMoz in these cases of quick research. I will use their free service for this example, which requires no log in, and they are even more generous with data when you register for a free account.
The first thing I do is head over to the anchor text distribution of the site or page to see if the site/page is attracting links specific to the keyword I am researching:
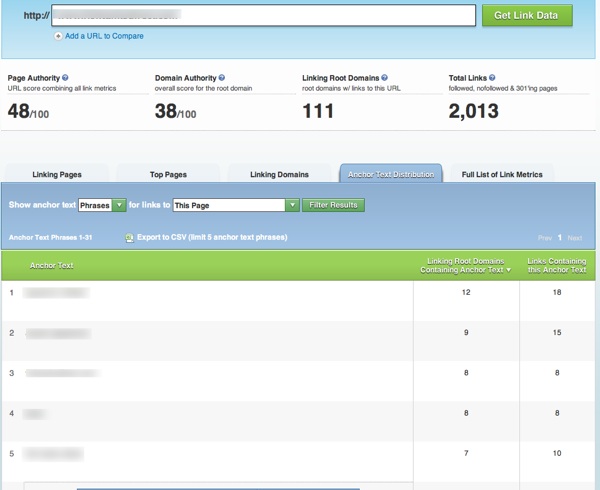
What’s great here is you can see the top 5 instances of anchor text usage, how many total links are using that term, and how many unique domains are supplying those total links.
You can also see data relative to the potential quality of the entire link profile in addition to the ratio of total/unique domains linking in.
You probably won’t want or need to do this for every single keyword you decide to pursue. However, when looking at a new market, a potential core keyword, or if you are considering buying an exact match domain for a specific keyword you can accomplish a really good amount of competitive research on that keyword by using a couple free tools.
Types of Competitive Research
Competitive research is a broad term and can go in a bunch of different directions. As an example, when first entering a market you would likely start with some keyword research and move into analyzing the competition of those keywords before you decide to enter or fully enter the market.
As you move into bigger markets and start to do more enterprise-level competitive research specific to a domain, link profiles, or a broader market you might move into some paid tools.
Analysis paralysis is a major issue in SEO. Many times you might find that those enterprise-level tools really are overkill for what you might be trying to do initially. Gauging the competitiveness of a huge keyword or a lower volume keyword really doesn’t change based on the money you throw at a tool. The data is the data especially when you narrow down the research to a keyword, keywords, or domains.
Get the Data, Make a Decision
So with the tools we used here you are getting many of the key data points you need to decide whether pursuing the keyword or keywords you have chosen is right for you.
Some things the tools cannot tell you are questions we talked about before:
- how much captial can you allocate to the project?
- how hard are you willing to work?
- do you have a network of contacts you can lean on for advice and assistance?
- do you have enough patience to see the project through, especially if ranking will take a bit..can you wait on the revenue?
- is creativity lacking in the market and can you fill that void or at least be better than what’s out there?
Only you can answer those questions :)


