Post-Panda: Data Driven Search Marketing

Now is the best and exciting time to be in marketing. The new data-driven approaches and infrastructure to collect customer data are truly changing the marketing game, and there is incredible opportunity for those who act upon the new insights the data provides” - Mark Jeffrey, Kellog School Of Management
I think Jeffries is right - now is one of the best and exciting times to be in marketing!
It is now cheap and easy to measure marketing performance, so we are better able to spot and seize marketing opportunities. If we collect and analyze the right data, we will make better decisions, and increase the likelihood of success.
As Google makes their system harder to game using brute force tactics, the next generation of search marketing will be tightly integrated with traditional marketing metrics such as customer retention, churn, profitability, and customer lifetime value. If each visitor is going to be more expensive to acquire, then we need to make sure those visitors are worthwhile, and the more we engage visitors post-click, the more relevant our sites will appear to Google.
We’ll look at some important metrics to track and act upon.
But first....
Data-Driven Playing Field
There is another good reason why data-driven thinking should be something every search marketer should know about, even if some search marketers choose to take a different approach.
Google is a data-driven company.
If you want to figure out what Google is going to do next, then you need to think like a Googler.
Googlers think about - and act upon - data.
`
Douglas Bowman, a designer at Google, left the company because he felt they placed too much reliance on data over intuition when it came to visual design decisions.
Yes, it’s true that a team at Google couldn’t decide between two blues, so they’re testing 41 shades between each blue to see which one performs better. I had a recent debate over whether a border should be 3, 4 or 5 pixels wide, and was asked to prove my case. I can’t operate in an environment like that. I’ve grown tired of debating such miniscule design decisions. There are more exciting design problems in this world to tackle
Regardless of whether you think acting on data or intuition is the right idea, if you can relate to the data-driven mindset and the company culture that results, you will better understand Google. Searcher satisfaction metrics are writ-large on Google’s radar and they will only get more refined and granular as time goes on.
Update Panda was all about user engagement issues. If a site does not engage users, it is less likely to rank well.
As Jim Boykin notes, Google are interested in the “long click”:
On the most basic level, Google could see how satisfied users were. To paraphrase Tolstoy, happy users were all the same. The best sign of their happiness was the “long click”. this occurred when someone went to a search result, ideally the top one, and did not return. That meant Google has successfully fulfilled the query. But unhappy users were unhappy in their own ways, most telling were the “short clicks” where a user followed a link and immediately returned to try again. “If people type something and then go and change their query, you could tell they aren’t happy,” says (Amit) Patel. “If they go to the next page of results, it’s a sign they’re not happy. You can use those signs that someone’s not happy with what we gave them to go back and study those cases and find places to improve search.
In terms of brand, the more well known you are, the more some of your traffic is going to be pre-qualified. Brand awareness can lower your bounce rate, which leads to better engagement signals.
Any site is going to have some arbitrary brand-related traffic and some generic search traffic. Where a site has good brand-related searches, those searches create positive engagement metrics which lift the whole of the site. The following chart is conceptual, but it drives the point home. As more branded traffic gets folded into the mix, aggregate engagement metrics improve.
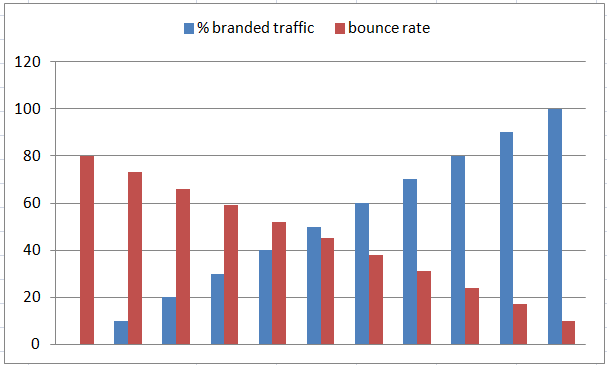
If your site and business metrics look good in terms of visitor satisfaction - i.e. people are buying what you offer and/or reading what you have to say, and recommending you to their friends - it’s highly likely your relevancy signals will look positive to Google, too. People aren’t just arriving and clicking back. They are engaging, spending time, talking about you, and returning.
Repeat visits to your site, especially from logged-in Google users with credit cards on file, are yet another signal Google can look at to see that people like, demand and value what you offer.
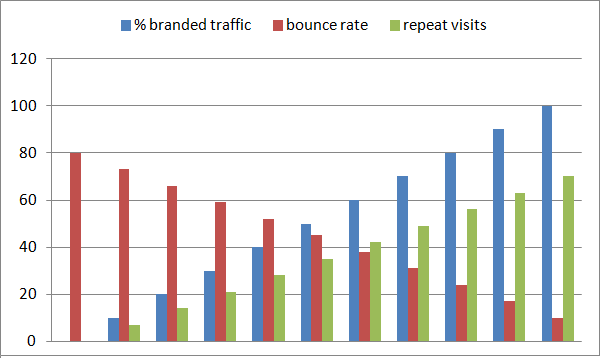
Post-Panda, SEO is about the behavior of visitors post-click. In order to optimize for visitor satisfaction, we need to measure their behavior post-click and adjust our offering. A model that I've found works well in a post-Panda environment is a data-driven approach, often used in PPC. Yes, we still have to do link building and publish relevant pages, but we also have to focus on the behavior of users once they arrive. We collect and analyze behavior data and feed it back into our publication strategy to ensure we're giving visitors exactly what they want.
What Is Data Driven Marketing?
Data driven marketing is, as the name suggests, the collection and analysis of data to provide insights into marketing strategies.
It’s a way to measure how relevant we are to the visitor, as the more relevant we are, the more positive our engagement metrics will be. A site can constantly be adapted, based on the behavior of previous visitors, in order to be made more even more relevant.
Everyone wins.
The process involves three phases. Setting up a framework to measure and analyze visitor behaviour, testing assumptions using visitor data, then optimizing content, channels and offers to maximize return. This process is used a lot in PPC.
Pre-web, this type of data used to be expensive to collect and analyse. Large companies engaged market researchers to run surveys, focus groups, and go out on the street to gather data.
These days, collecting input from consumers and adapting campaigns is as easy as firing up analytics and creating a process to observe behaviour and modify our approach based on the results. High-value data analysis and marketing can be done on small budgets.
Yet many companies still don’t do it.
And many of those that do aren’t measuring the right data. By capturing and analysing the right data, we put ourselves at a considerable advantage to most of our competitors.
In his book Data Driven Marketing, Jeffrey notes that the lower performing companies in the Fortune 500 were spending 4% less than the average on marketing, and the high performers were investing 20% more than average. Low performers focused on demand generation - sales, coupons, events - whereas high performers spend a lot more on brand and marketing infrastructure. Infrastructure includes the processes and software tools needed to capture and analyse marketing data.
So the more successful companies are spending more on tools and process than lower performing companies.
When it comes to the small/medium sized businesses, we have most of the tools we need readily available. Capturing and analyzing the right data is really about process and asking the right questions.
What Are The Right Questions?
We need a set of metrics that help us measure and optimize for visitor satisfaction.
Jeffrey identifies 15 data-analysis areas for marketers. Some of these metrics relate directly to search marketing, and some do not. However, it’s good to at least be aware of them as these are the metrics traditional marketing managers use, so might serve as inspiration get us thinking about where the cross-overs into search marketing lay. I recommend reading his book to anyone who wants a crash course in data-driven marketing and to better understand where how marketing managers think.
- Brand awareness
- Test Drive
- Churn
- Customer satisfaction
- Take rate
- Profit
- Net Present Value
- Internal Rate Of Return
- Payback
- Customer Lifetime Value
- Cost Per Click
- Transaction Conversion Rate
- Return On Ad Dollars Spent
- Bounce Rate
- Word Of Mouth (Social Media Reach)
I’ll re-define this list and focus on a few metrics we could realistically use that help us optimize sites and offers in terms of visitor engagement and satisfaction. As a bonus, we’ll likely create the right relevancy signature Google is looking for which will help us rank well. Most of these metrics come directly from PPC.
First, we need a.....dashboard! Obviously, a dashboard is a place where you can see how you’re progressing, at a glance, measured over time. There are plenty of third party offerings, or you can roll-your-own, but the important thing is to have one and use it. You need a means to measure where you are, and where you’re going in terms of visitor engagement.
1. Traffic Vs Leads
Traffic is a good metric for display and brand purposes. If a site is making money based on how many people see the site, then they will be tracking traffic.
For everyone else, combining the two can provide valuable insights. If traffic has increased, but the site is generating the same number of leads - or whatever your desired engagement action may be, but I'll use the term "leads" to mean any desired action - then is that traffic worthwhile? Track how many leads are closed and this will tell you if the traffic is valuable. If the traffic is high, but engagement is low, then visitors are likely clicking back, and this is not a signal Google deems favorable.
This data is also the basis for adjusting and testing the offer and copy. Does engagement increase or decrease after you’ve adjusted the copy and/or the offer?
2. Search Channel Vs Other Channels
Does search traffic result in more leads than, say, social media traffic? Does it result in more leads vs any other channel? If so, then there is justification to increase spending on search marketing vs other channels.
Separate marketing channels out so you can compare and contrast.
3. Channel Growth
Is the SEM channel growing, staying the same, or declining vs other channels?
Set targets and incremental milestones. Create a process to adjust copy and offers and measure the results. The more conversions to desired action, the better your relevancy signal is likely to be, and the more you’ll be rewarded.
You can get quite granular with this metric. If certain pages are generating more leads than others as the direct result of keyword clicks, then you know which keyword areas to grow and exploit in order to grow the performance of the channel as a whole. It can be difficult to isolate if visitors skip from page to page, but it can give you a good idea which entry pages and keywords kick it all off.
4. Paid Vs Organic
If a search campaign is running both PPC and SEO, then split these two sources out. Perhaps SEO produces more leads. In which case, this will justify creating more blog posts, articles, link strategies, and so on.
If PPC produces more leads, then the money may be better spent on PPC traffic, optimizing offers and landing pages, and running A/B tests. Of course, the information gleaned here can be fed into your organic strategies. If the content works well in PPC, it is likely to work well in SEO, at least in terms of engagement.
5. Call To Action
How do you know if a call to action is working? Could the call to action be worded differently? Which version of the call to action works best? Which position does it work best? Does the color of the link make a difference?
This type of testing is common in PPC, but less so in SEO. If SEO pages are optimized in this manner, then we increase the level of engagement and reduce the click-back.
6. Returning Visitor
If all your visitors are new and never return, then your broader relevance signals aren’t likely to be great.
This doesn’t mean all sites must have a high number of return visitors in order to deemed relevant - one-off sales sites would be unlikely to have return visitors, yet a blog would - however, if your site is in a class of sites where every other site listed is receiving return visits, then your site is likely to suffer by comparison.
Measure the number of return visitors vs new visitors. Think about ways you can keep visitors coming back, especially if you suspect that your competitors have high return visitor rates.
7. Cost Per Click/Transaction Conversion Rate/Return On Ad Dollars Spent
PPC marketers are familiar with these metrics. We pay per click (CPC) and hope the visitor converts to desired action. We get a better idea of the effectiveness of keyword marketing when we combine this metric with transaction conversion rate (TCR) and return on ad dollars spent (ROA). TCR = transaction conversion rate; the percentage of customers who purchase after clicking through to your website. ROA = return on ad dollars spent.
These are good metrics for SEOs to get their heads around, too, especially when justifying SEO spends relative to other channels. For cost per click, use the going rate on Adwords and assign it to the organic keyword if you want to demonstrate value. If you're getting visitors in at a lot lower price per click the SEO channel looks great. The cost-per-click in SEO is also the total cost of the SEO campaign divided by clicks over time.
8. Bounce Rate
Widely speculated to be an important metric post-Panda. Obviously, we want to get this rate down, Panda or not.
If you’re seeing good rankings but high bounce rates for pages it’s because the page content isn’t relevant enough. It might be relevant in terms of content as far as the algorithm sees it, but not relevant in terms of visitor intent. Such a page may drift down the rankings over time as a result, and it certainly doesn’t do other areas of your business any good
9. Word Of Mouth (Social Media Reach/Brand)
Are other people talking about you? Do they repeat your brand name? Do they do so often? If you can convince enough people to search for you based on your name, then you’ll “own” that word. Google must return your site, else they’ll be seen as lacking.
Measuring word-of-mouth used to be difficult but it’s become a lot easier, thanks to social media and the various information mining tools available. Aaron has written a lot on the impact of brand in SEO, so if this area is new to you, I’d recommend reading back through The Rise Of Brand Over Time, Big Brands and Potential Brand Signals For Panda.
10. Profit
It’s all about the bottom line.
If search marketers can demonstrate they add value to the bottom line, then they are much more likely to be retained and have budget increased. This isn't directly related to Panda optimization, other than in the broad sense that the more profitable the business, the more likely they are keeping visitors satisfied.
Profit = revenue - cost. Does the search marketing campaign bring in more revenue that it costs to run? How will you measure and demonstrate this? Is the search marketing campaign focused on the most profitable products, or the least? Do you know which products and services are the most profitable to the business? What value does your client place on a visitor?
There is no one way of tracking this. It’s a case of being aware of the metric, then devising techniques to track it and add it to the dashboard.
11. Customer Lifetime Value
Some customers are more important than others. Some customers convert, buy the least profitable service or product, and we never hear from them again. Some buy the most profitable service or product, and return again and again.
Is the search campaign delivering more of the former, or the latter? Calculating this value can be difficult, and relies on internal systems within the company that the search marketer may not have access to, but if the company already has this information, then it can help validate the cost of search marketing campaigns and to focus campaigns on the keyword areas which offer the most return.
Some of these metrics don't specifically relate to ranking, they're about marketing value, but perhaps an illustration of how some of the traditional marketing metrics and those of search marketers are starting to overlap. The metrics I've outlined are just some of the many metrics we could use and I'd be interested to hear what other metrics you're using, and how you're using them.
Optimizing For Visitor Experience
If you test these metrics, then analyse and optimize your content and offers based on your findings, not only will this help the bottom line, but your signature on Google, in terms of visitor relevance, is likely to look positive because of what the visitor does post-click.
When we get this right, people are engaging. They are clicking on the link, they’re staying rather than clicking back, they’re clicking on a link on the page, they’re reading other pages, they’re interacting with our forms, they’re book-marking pages or telling others about our sites on social media. These are all engagement signals, and increased engagement tends to indicate greater relevance.
This is diving deeper than a traditional SEO-led marketing approach, which until quite recently worked, even if you only operated in the search channel and put SEO at the top of the funnel. It’s not just about the new user and the first visit, it’s also about the returning visitor and their level of engagement over time. The search visitor has a value way beyond that first click and browse.
Data-driven content and offer optimization is where SEO is going.
New to the site? Join for Free and get over $300 of free SEO software.



Once you set up your free account you can comment on our blog, and you are eligible to receive our search engine success SEO newsletter.
Already have an account? Login to share your opinions.




Comments
Add new comment